lv länderabkürzung | länderkürzel in
$241.00
In stock
The world is a complex tapestry of nations, each with its own unique identity, culture, and administrative structure. In this interconnected global landscape, efficient communication and data management are paramount. This is where country codes, or *Länderabkürzungen* in German, play a crucial role. These standardized codes, meticulously defined and maintained by international organizations, provide a universal language for identifying and referencing countries in various contexts, from international trade and postal services to sports competitions and online communication. This article delves into the world of country codes, focusing on the ISO 3166-1 standard and exploring the different types of codes, their applications, and their significance in the modern world.
The Cornerstone: ISO 3166-1 and its Structure
At the heart of the global country code system lies the ISO 3166-1 standard, meticulously crafted and maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). First introduced in 1974, this standard provides a comprehensive list of country codes, meticulously organized and regularly updated to reflect the ever-changing geopolitical landscape. ISO 3166-1 is not just a simple list; it's a structured framework that categorizes countries using three distinct code systems:
* ALPHA-2 Codes: These two-letter codes are arguably the most widely recognized and used country codes. Think of them as the shorthand of international communication. They are employed in numerous applications, including:
* Internet Domain Names: The familiar ".uk" for the United Kingdom, ".de" for Germany, and ".fr" for France are all examples of ALPHA-2 codes used as Top-Level Domains (TLDs).
* Currency Codes: The Euro's official currency code, "EUR," often incorporates the ALPHA-2 code of the countries within the Eurozone.
* International Trade: Customs declarations and shipping documents frequently utilize ALPHA-2 codes to identify the origin and destination of goods.
* Travel Documents: Passports and visas often incorporate ALPHA-2 codes to indicate the issuing country.
* ALPHA-3 Codes: These three-letter codes offer a more extensive and less ambiguous representation of countries. While not as ubiquitous as ALPHA-2 codes, they are widely used in:
* Statistical Analysis: Government agencies and international organizations often rely on ALPHA-3 codes for data analysis and reporting.
* Database Management: ALPHA-3 codes provide a unique identifier for countries in large databases, minimizing the risk of confusion.
* Computer Systems: Many software applications and programming languages utilize ALPHA-3 codes for country-specific settings and configurations.
* Numeric Codes: These three-digit numeric codes provide a language-independent representation of countries. They are particularly useful in:
* Data Processing: Numeric codes simplify data processing and sorting, especially in systems that may not support alphabetic characters.
* International Organizations: Organizations like the United Nations often use numeric codes for internal reporting and data management.
* Legacy Systems: Some older systems may rely solely on numeric codes for compatibility reasons.
The ISO 3166-1 standard is more than just a collection of codes; it's a dynamic system that reflects the changing world. New countries are added as they gain international recognition, and codes may be modified or withdrawn as geopolitical situations evolve. Regular updates ensure that the standard remains accurate and relevant.
Beyond ISO 3166-1: Other Important Country Code Systems
While ISO 3166-1 is the most widely recognized and comprehensive standard, other organizations maintain their own country code systems for specific purposes. These include:
* IOC Country Codes (International Olympic Committee): The IOC uses its own set of three-letter codes to represent countries participating in the Olympic Games. These codes are often similar to, but not always identical to, the ISO 3166-1 ALPHA-3 codes. For example, Germany is represented as GER by ISO but as GER by the IOC.
* FIFA Country Codes (Fédération Internationale de Football Association): Similar to the IOC, FIFA uses its own three-letter codes for representing countries in international football competitions. Again, there can be variations from the ISO standard.
* NATO Country Codes: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) maintains its own set of codes for member states and other countries involved in its activities.
* E.164 Country Codes: These are the dialing codes used for international telephone calls. Each country is assigned a unique code that must be dialed before the local number.
Understanding the differences between these various code systems is crucial to avoid confusion and ensure accurate data interpretation.
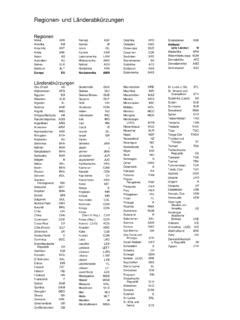
Länderkürzel Tabelle (Country Code Table): A Visual Guide
A *Länderkürzel Tabelle* (country code table) is a valuable resource for quickly looking up the various codes associated with a specific country. These tables typically include the ALPHA-2, ALPHA-3, and numeric codes from ISO 3166-1, as well as codes from other relevant organizations like the IOC and FIFA. Many online resources provide up-to-date and searchable country code tables.
Länderkürzel Liste (Country Code List): A Comprehensive Inventory
Additional information
| Dimensions | 5.2 × 1.9 × 1.6 in |
|---|