lv installation | lvl beam installation guide
$209.00
In stock
The flow of electricity, from the power plant to the devices we use every day, is a complex and carefully orchestrated process. While most people are familiar with the electrical outlets in their homes and offices, they may not fully understand the intricate infrastructure that delivers that power. Central to this infrastructure are two distinct, yet interconnected, systems: Low Voltage (LV) distribution and structural support systems, like those incorporating Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) beams.
This article delves into the world of LV installation, exploring its crucial role in power delivery and examining the integration of LVL beams for structural support, particularly in residential and commercial construction. We will cover everything from the fundamentals of LV distribution to the practical aspects of LVL beam installation, providing a comprehensive guide for homeowners, contractors, and anyone interested in understanding these essential building components.
I. Understanding Low Voltage (LV) Distribution
A home or business typically draws power to its main electrical panel from a transformer or overhead wires connected to poles. These transformers and poles, in turn, get their power from a power company's electrical substation. The journey of electricity from the substation to your outlets involves different voltage levels. High-voltage transmission lines carry electricity over long distances with minimal loss, but these voltages are far too high for direct use in homes and businesses. This is where LV distribution comes into play.
What is LV Distribution?
Low Voltage (LV) distribution refers to the final stage of power delivery, where electricity is stepped down to a usable voltage level (typically 120/240V in North America and 230/400V in Europe) and distributed to individual circuits within a building. This involves a network of transformers, distribution panels, circuit breakers, wiring, and outlets.
Why is LV Distribution Important?
LV distribution is critical for several reasons:
* Safety: High voltage electricity is extremely dangerous. Stepping down the voltage to a safe level for residential and commercial use is paramount.
* Efficiency: Electrical devices are designed to operate at specific voltage levels. LV distribution ensures that appliances and equipment receive the correct voltage, optimizing their performance and preventing damage.lv installation
* Control: LV distribution allows for the control and protection of individual circuits. Circuit breakers and fuses protect against overloads and short circuits, preventing fires and electrical hazards.
* Reliability: A well-designed LV distribution system provides a reliable and consistent power supply, minimizing disruptions and ensuring that electrical devices function properly.
Key Components of an LV Distribution System:
* Transformers: These devices step down the voltage from the utility grid to the usable voltage level for the building. They are typically located outside the building or in a dedicated electrical room.
* Main Electrical Panel: This is the central point of the LV distribution system. It receives power from the transformer and distributes it to individual circuits via circuit breakers.
* Circuit Breakers: These are safety devices that protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. When a circuit breaker trips, it interrupts the flow of electricity, preventing damage to wiring and appliances.
* Wiring: The wiring system carries electricity from the main electrical panel to outlets, switches, and appliances throughout the building. Different types of wiring are used for different applications, depending on the amperage and voltage requirements.
* Outlets and Switches: These are the points where electrical devices are connected to the power supply. They are designed to provide a safe and convenient way to access electricity.
II. Integrating LVL Beams into Structural Design: A Comprehensive Guide
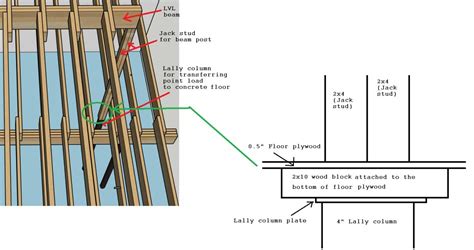
While LV distribution focuses on the electrical infrastructure, the structural integrity of a building is equally important. In many modern construction projects, Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) beams are utilized for their strength, stability, and versatility. Understanding how to properly install LVL beams is crucial for ensuring the safety and longevity of the structure.
What are LVL Beams?
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) is an engineered wood product made by bonding thin wood veneers together under heat and pressure. The veneers are oriented with the grain running parallel to the length of the beam, resulting in a strong, consistent, and predictable structural member.
Why Use LVL Beams?
LVL beams offer several advantages over traditional solid lumber:
* Strength: LVL beams are significantly stronger than solid lumber of the same size. This allows for longer spans and reduced support requirements.
* Stability: LVL beams are less prone to warping, twisting, and shrinking than solid lumber. This makes them ideal for applications where dimensional stability is critical.
* Consistency: The manufacturing process ensures that LVL beams have consistent strength and quality throughout their length. This allows for more accurate structural calculations and design.
* Versatility: LVL beams can be cut, drilled, and shaped to meet specific design requirements.
* Environmentally Friendly: LVL beams can be manufactured from sustainably harvested wood resources.
III. LVL Beam Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing LVL beams requires careful planning, precise measurements, and adherence to building codes and manufacturer's instructions. The following guide provides a general overview of the installation process. Always consult with a qualified structural engineer and local building codes before beginning any structural work.
A. Planning and Preparation:
Additional information
| Dimensions | 5.4 × 3.9 × 1.6 in |
|---|