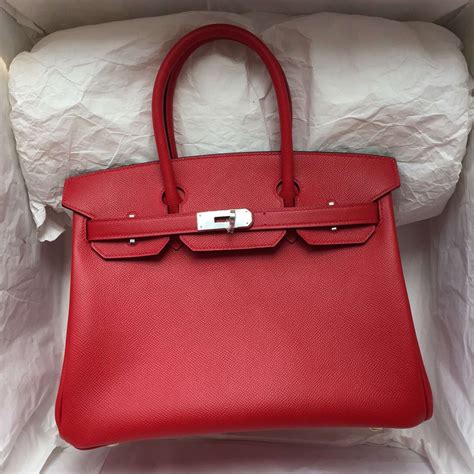
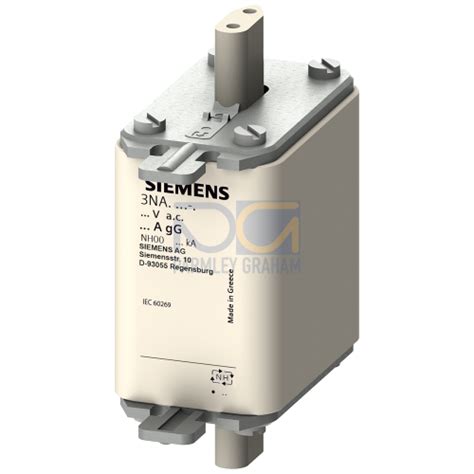
lv hrc | Lv hrc fuse
$229.00
In stock
Low-Voltage High Rupturing Capacity (LV HRC) fuses are crucial components in low-voltage electrical distribution systems, providing robust protection against overcurrents and short circuits. These fuses are designed to interrupt high fault currents quickly and safely, preventing damage to equipment, minimizing downtime, and ensuring the safety of personnel. In particular, Siemens LV HRC fuses, part of their comprehensive SENTRON 3NA range, offer reliable and effective protection, backed by a legacy of engineering excellence and adherence to stringent international standards. This article will delve into the functionality, types, applications, selection criteria, and advantages of LV HRC fuses, with a specific focus on Siemens' offerings.
Understanding LV HRC Fuses: The Fundamentals
At its core, an LV HRC fuse is a current-limiting, overcurrent protection device. It consists of a fuse element (typically made of silver or copper alloys) enclosed within a body, usually ceramic or fiberglass, filled with a quenching medium, often quartz sand. When an overcurrent or short circuit occurs, the fuse element melts, interrupting the circuit and clearing the fault. The design of the fuse, including the material, shape, and dimensions of the fuse element, and the properties of the quenching medium, are critical in determining its performance characteristics.
The "High Rupturing Capacity" aspect is particularly significant. It refers to the fuse's ability to safely interrupt extremely high fault currents without causing an explosion or arc flash. This is achieved through a combination of factors:
* Fuse Element Design: The shape and configuration of the fuse element are engineered to control the arc that forms during interruption. Often, these elements have notches or constrictions that create multiple, smaller arcs, which are easier to extinguish.
* Quenching Medium: The quartz sand acts as a heat sink and deionizing agent, rapidly cooling and extinguishing the arc. It also helps to prevent the formation of conductive paths that could allow the fault current to continue flowing.
* Body Material: The ceramic or fiberglass body provides mechanical strength and thermal insulation, preventing the fuse from shattering during a high-fault event and containing any hot gases or molten metal.
Key Characteristics and Parameters of LV HRC Fuses
Understanding the key characteristics of LV HRC fuses is crucial for proper selection and application. These parameters define the fuse's performance and suitability for a specific electrical circuit.
* Rated Voltage (Ur): This is the maximum voltage at which the fuse is designed to operate. It must be equal to or greater than the system voltage. Exceeding the rated voltage can lead to premature failure or reduced interrupting capacity.
* Rated Current (In): This is the continuous current that the fuse can carry without deterioration or opening. It should be carefully selected based on the expected load current of the protected circuit, considering factors like ambient temperature and derating.lv hrc
* Breaking Capacity (Icn): This is the maximum prospective short-circuit current that the fuse can safely interrupt under specified conditions. It's a critical parameter for ensuring the fuse can handle the highest possible fault current in the system. The breaking capacity must be greater than the maximum fault current at the point of installation.
* Time-Current Characteristic (TCC): This curve illustrates the relationship between the current flowing through the fuse and the time it takes to interrupt the circuit. It provides valuable information for coordinating fuses with other protective devices, such as circuit breakers, to ensure selective tripping and minimize downtime.
* I²t Value: This represents the let-through energy of the fuse, which is the amount of energy released during the interruption of a fault current. A lower I²t value indicates better protection for downstream equipment, as it limits the thermal stress imposed on them.
* Operating Class (gG, aM, gR, etc.): This classification indicates the fuse's intended application and performance characteristics. Common operating classes include:
* gG (gL): General purpose fuses for protecting cables, conductors, and equipment against overload and short circuits.
* aM: Fuses for motor circuit protection, offering short-circuit protection and often used in conjunction with motor overload relays.
* gR (aR): Fuses for semiconductor protection, designed to interrupt very fast-rising short-circuit currents in power semiconductor applications.
Siemens LV HRC Fuses: The SENTRON 3NA Range
Siemens, a global leader in electrical engineering and electronics, offers a comprehensive range of LV HRC fuses under the SENTRON 3NA series. These fuses are designed and manufactured to meet the highest quality standards, ensuring reliable and effective protection for a wide range of applications.
The SENTRON 3NA range encompasses various fuse sizes, operating classes, and voltage ratings, catering to diverse requirements in industrial, commercial, and residential installations. Key features of Siemens LV HRC fuses include:
* High Breaking Capacity: Siemens fuses are designed to interrupt high fault currents, providing robust protection even in demanding applications.
* Precise Time-Current Characteristics: The TCC curves are accurately defined and readily available, facilitating proper coordination with other protective devices.
* Low I²t Values: Siemens fuses minimize let-through energy, protecting downstream equipment from thermal stress and potential damage.
Additional information
| Dimensions | 8.3 × 1.1 × 2.4 in |
|---|